Laparoscopic Gb/Stones(Gallbladder Stones) Surgery in Pune
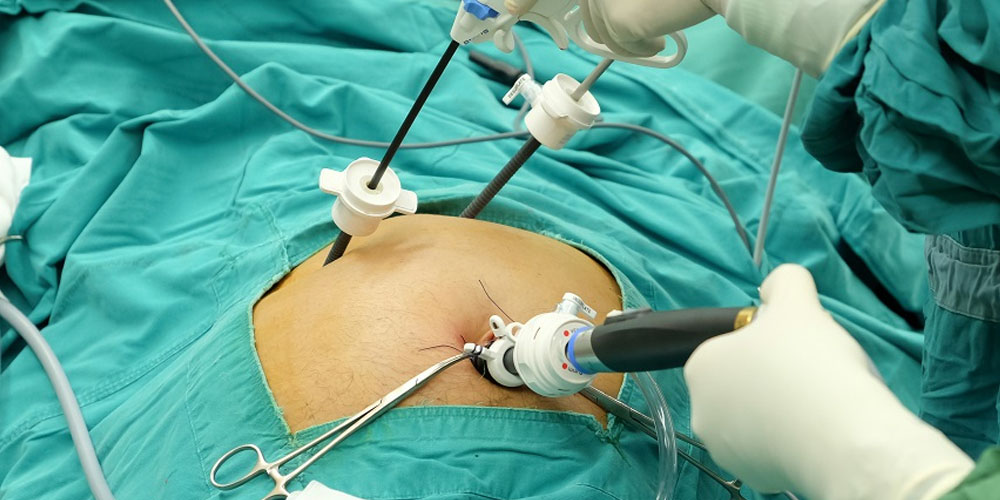
Three to four small cuts are made in your abdomen. One cut (between 2-3cm) will be by the belly button and the others (each about 1cm or less) will be on the right side of your abdomen. Your abdomen is inflated using carbon dioxide gas. A laparoscope (a long, thin telescope with a tiny light and video camera at the end) is inserted through one of the cuts in your abdomen. This allows your surgeon to view the operation on a video monitor. Your surgeon will then remove your gallbladder using special surgical instruments. After the gallbladder has been removed, the gas in your abdomen will escape through the laparoscope. The cuts in your skin are closed with dissolvable stitches and covered with dressings. The operation takes 60 to 90 minutes.
The gallbladder is a small, pouch-like organ situated underneath the liver. The main purpose of the gallbladder is to store and concentrate bile. The bile is stored in the gallbladder and over time it becomes more concentrated, which makes it better at digesting fats.
What causes gallstones?
It is thought that gallstones develop because of an imbalance in the chemical make-up of bile inside the gallbladder. In most cases, the levels of cholesterol in bile become too high and the excess cholesterol forms into stones. Gallstones are very common. You are more at risk of developing gallstones if you are:
- Overweight or obese
- Female – women are two to three times more likely to be affected by gallstone disease than men
- 40 or over
- A mother – women who have had children have an increased risk of gallstone disease, which may be because the hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy increase cholesterol levels
